Have you ever woken up feeling mentally refreshed, like your brain just had a deep clean? That’s more than just a feeling—it’s a biological process called glymphatic drainage. This natural detox system is essential for clearing out waste, toxins, and other byproducts from your brain while you sleep, helping to maintain brain health and function.
As research into brain health expands, scientists are discovering just how vital glymphatic drainage is for maintaining long-term cognitive function, preventing disease, and achieving overall mental clarity. Disruptions to this process, such as poor sleep, can lead to a buildup of toxins associated with conditions like Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what the glymphatic system does, why proper sleep is essential for brain detoxification, and practical ways you can naturally support and enhance this process. By optimizing glymphatic drainage, you can boost brain performance and preserve cognitive health in the long run.
Understanding the Glymphatic System
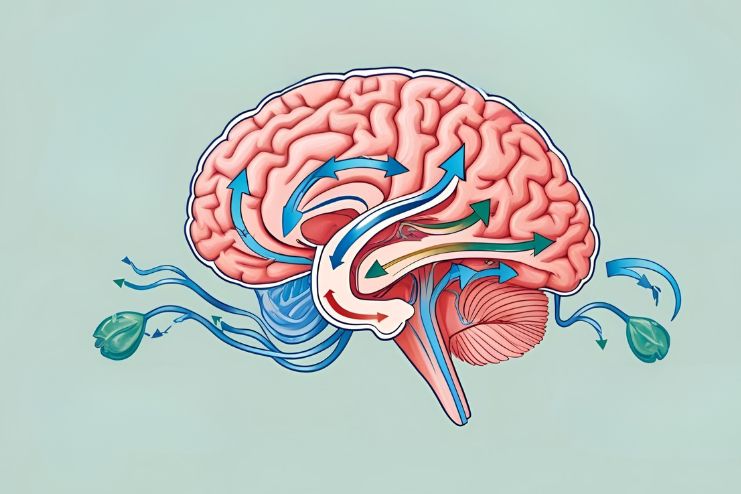
Your body has the lymphatic system to remove waste, but your brain relies on a specialized network called the glymphatic system. This system is responsible for clearing metabolic waste, toxins, dead cells, and other byproducts from your brain while you’re sleeping. It primarily operates by using cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flush these harmful substances out of the brain tissue.
The glymphatic system acts much like the lymphatic system found throughout the rest of the body, but is unique to the brain. It plays a crucial role in maintaining brain homeostasis and contributes to brain immunity by helping transport antigens and immune cells.
How the Glymphatic System Works
The glymphatic system is most active during deep sleep. When you’re in deep sleep, cerebrospinal fluid flows through specific brain pathways, removing harmful substances like beta-amyloid plaques and tau proteins—both of which are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. By efficiently removing these waste products, the glymphatic system supports cognitive health, helping to maintain sharpness and clarity of thought.
Key Functions of the Glymphatic System
- Waste Removal: The system clears metabolic waste products and toxic substances from brain tissue.
- Fluid Transport: It facilitates the movement of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid (ISF) within the brain.
- Brain Homeostasis: The glymphatic system helps maintain a stable internal environment in the brain.
- Brain Immunity: It may also assist in transporting immune cells, contributing to the brain’s overall immune health.
Without efficient glymphatic drainage, waste can build up in the brain, increasing the risk of issues like brain fog, cognitive decline, and even neurodegenerative diseases.
Importance of the Glymphatic System
The glymphatic system’s ability to remove metabolic waste is key to preventing the buildup of harmful substances that can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. This self-cleaning mechanism works best while you’re in deep sleep, emphasizing the importance of sleep for brain health. Dysfunction in the glymphatic system is associated with various neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Researchers are continuing to explore how optimizing this system could potentially lead to therapeutic treatments for these conditions. Understanding and enhancing glymphatic function may hold the key to better brain health and longer-lasting cognitive function.
The Link Between Sleep and Brain Detox

Did you know that the quality of your sleep directly impacts your brain’s ability to detoxify? It’s during deep sleep that your brain undergoes a natural “cleaning” process, with the glymphatic system working its hardest to flush out toxins and waste products that accumulate throughout the day. Without this crucial detox, toxins can build up, potentially affecting your mental clarity and long-term brain health.
READ MORE: Understanding REM Sleep: Why It’s Critical for Brain Health
Best Sleep Positions for Glymphatic Flow
The glymphatic system is most active during slow-wave sleep or deep sleep. During this phase, your brain cells shrink, creating more space for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flow through and efficiently remove harmful substances like beta-amyloid plaques, which are linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
If you’re not getting enough deep sleep, this waste removal slows down, increasing the risk of cognitive decline and memory issues over time. Here are a few sleep positions you should try and incorporate to ensure a good brain detox:
- Side Sleeping (Left or Right): Studies suggest that sleeping on your side is the most effective position for promoting glymphatic drainage and brain detox.
- Back Sleeping: Although less effective than side sleeping, back sleeping still allows for some glymphatic function and is better than sleeping on your stomach.
- Stomach Sleeping: This position may restrict glymphatic activity due to poor cerebrospinal fluid flow, making it the least effective for brain detox.
How Sleep Supports Brain Detoxification
During sleep, your brain is hard at work—not just resting but actively cleaning itself. The glymphatic system acts like a “brain plumbing system,” using CSF to flush out toxins and metabolic waste. This system ramps up significantly during sleep, especially deep sleep, when brain cells shrink and allow more room for the fluid to wash away waste.
One fascinating aspect of this process is that brain waves generated during sleep help propel the fluid through the brain, essentially aiding in the removal of harmful debris. If your sleep is disrupted or of poor quality, this detoxification process becomes less efficient, potentially leading to the buildup of harmful proteins that are linked to neurological diseases.
READ MORE: Depth Of Sleep Does Have Impacts On Brain’s Cleaning
Prioritizing Sleep for Brain Health
Sleep isn’t just about resting—it’s a vital time for your brain to detox and restore itself. By prioritizing quality sleep, you support your brain’s natural ability to remove toxic waste and maintain cognitive health. Whether it’s finding the right sleep position or improving your overall sleep habits, ensuring that you get enough deep, restful sleep is key to keeping your brain healthy and sharp.
Toxins and Waste Cleared by the Glymphatic System

Every day, your brain works tirelessly, generating waste as a byproduct of its complex processes. Without an efficient system to clear this waste, harmful substances can accumulate, contributing to neurological issues and cognitive decline. The glymphatic system is like your brain’s natural cleaning crew, working primarily during sleep to flush out toxins and maintain optimal brain health.
Some of the most critical waste products it clears include:
- Beta-Amyloid Plaques – These toxic proteins are closely associated with Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive impairment.
- Tau Proteins – Another harmful protein linked to neurodegenerative diseases like dementia and Parkinson’s.
- Metabolic Waste – Byproducts of everyday brain activity that, if left unchecked, can lead to inflammation and other harmful effects.
By promoting efficient glymphatic function through quality sleep, you can enhance your brain’s ability to clear these toxins, protecting against long-term neurological disorders and ensuring sharper cognitive health.
How to Support Your Glymphatic System

Maintaining a healthy glymphatic system is crucial for long-term brain health. By focusing on key lifestyle habits, you can optimize this brain detox system and reduce the risk of cognitive decline. Here are some practical ways to enhance glymphatic function:
Optimizing Sleep: Since the glymphatic system is most active during sleep, prioritizing rest is essential:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow for deep, restorative sleep cycles.
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule to support your natural circadian rhythm.
- Reduce blue light exposure before bed to boost melatonin production, which enhances sleep quality.
READ MORE: 12 Scientifically Proven Tips on How to Have Better Sleep at Night
Hydration & Nutrition: What you consume directly impacts your glymphatic function:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, which helps maintain the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Incorporate brain-boosting foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and turmeric, all known for their neuroprotective benefits.
- Limit alcohol and processed foods that can impair glymphatic efficiency.
Exercise & Movement: Physical activity promotes circulation, which supports brain detox:
- Regular cardiovascular exercise improves blood flow and glymphatic function. Aim for at least 30 minutes most days.
- Simple movements, such as yoga and stretching, can help stimulate lymphatic and glymphatic flow.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage: Some techniques may directly aid in glymphatic support:
- Neck massages and acupressure techniques are believed to encourage lymphatic and glymphatic flow.
- Emerging research suggests that craniosacral therapy may also assist in brain detoxification, although more evidence is needed.
Intermittent Fasting & Brain Health: Fasting activates your body’s natural detox processes:
- Short periods of intermittent fasting (12-16 hours) may enhance glymphatic function by promoting autophagy, the process which your body clears out damaged cells.
By focusing on quality sleep, staying hydrated, eating a brain-healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise, you can actively support your glymphatic system and protect your brain from long-term damage.
Signs of a Sluggish Glymphatic System

When the glymphatic system, responsible for clearing waste from the brain, isn’t functioning at its best, it can lead to various issues. Recognizing the signs early on allows you to take steps to support this vital detox pathway.
- Brain Fog & Cognitive Fatigue: One of the most common signs is feeling mentally sluggish, struggling with focus, or experiencing a general sense of brain fog. This happens when waste products, such as beta-amyloid and tau proteins, accumulate in the brain.
- Poor Memory & Concentration: Impaired glymphatic function can make it harder to retain information or stay alert. The build-up of toxins in the brain affects cognitive performance, memory, and concentration.
- Mood Changes: A sluggish glymphatic system can also impact your emotional well-being. The accumulation of toxins in the brain may lead to neuroinflammation, contributing to mood swings, depression, anxiety, or increased irritability.
- Sleep Disruptions: Since the glymphatic system is most active during sleep, disruptions in your sleep patterns—such as insomnia or excessive daytime drowsiness—could be a sign that your brain’s detox process isn’t working as it should.
- Increased Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Long-term dysfunction of the glymphatic system can raise your risk for neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases. When toxic proteins aren’t cleared effectively, they accumulate and can play a role in the progression of these diseases.
By recognizing these warning signs early, you can take proactive measures to support your brain’s detox pathways and maintain optimal cognitive health.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the glymphatic system plays a vital yet often overlooked role in maintaining brain health by flushing out harmful toxins and waste products. From beta-amyloid plaques linked to Alzheimer’s to everyday metabolic waste, this system ensures the brain stays clean and functional. However, poor sleep, dehydration, and lack of movement can slow down this process, potentially leading to cognitive decline, memory problems, and even neurodegenerative diseases over time.
To keep your glymphatic system in top shape, prioritizing quality sleep, staying hydrated, eating brain-friendly foods, and engaging in regular exercise are key. Simple lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, sleeping on your side, or trying intermittent fasting, can all support better brain detox.
Recognizing the early signs of glymphatic dysfunction—like brain fog, poor memory, and mood swings—can prompt you to make these adjustments before more serious issues arise. In a world where brain health is becoming increasingly important, understanding and optimizing your glymphatic system can be a powerful tool for long-term cognitive well-being. By making small, proactive changes, you’re giving your brain the best chance to function at its highest potential.
Healthy sleep, healthy mind, better life.
References
- The Glymphatic System – A Beginner’s Guide
- Neurons Help Flush Waste Out of the Brain During Sleep
- Brain May Flush Out Toxins During Sleep
- The Brain’s Waste-Removal System
- Harnessing the Glymphatic System to Improve Brain Health
- Achieving Brain Clearance and Preventing Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices
In this Article