In a world that never slows down, the ability to focus has become one of the most powerful skills you can cultivate. Whether you’re a college student pulling an all-nighter, a working professional navigating a barrage of meetings, or someone simply trying to be more present and productive in daily life, maintaining mental clarity is critical. Yet, sustaining focus isn’t always easy. Modern life demands quick decisions and faster responses, leaving little room for mental fatigue or sluggishness.
Enter the age-old champion—caffeine—the beloved stimulant fueling millions of people through hectic schedules. Found in everything from your morning cup of coffee to high-energy sodas, caffeine has been a go-to solution for generations. At the same time, nootropics, often called “smart drugs,” are gaining attention as brain-boosting alternatives designed to enhance mental performance without the side effects associated with stimulants like caffeine.
These cognitive enhancers promise sustained focus, better memory, and even neuroprotection over the long haul. But between the quick fix of caffeine and the long-term support of nootropics, which one truly stands out? Should you cling to your espresso ritual, or is it time to explore new-age brain boosters?

In this deep dive, we’ll explore the science behind both, compare their benefits and drawbacks, highlight the best nootropics for focus, discuss nootropic-caffeine stacks, and help you choose what’s right for your brain—and your lifestyle.
Understanding How Caffeine Affects the Brain

Caffeine remains the undisputed king of mental performance enhancers, with over 80% of adults worldwide consuming it daily in some form (Heckman, Weil, & Gonzalez de Mejia, 2010). Coffee, tea, energy drinks, chocolate—you name it, caffeine is there, providing that much-needed jolt when focus wanes. But what exactly happens in your brain when you sip that first aromatic cup?
Mechanism of Action
Caffeine primarily works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter responsible for promoting sleep and relaxation. By occupying these receptors, caffeine effectively prevents drowsiness, leading to increased wakefulness and alertness (Fredholm et al., 1999).
Beyond just adenosine, caffeine also enhances the release of dopamine and norepinephrine, the same neurotransmitters linked to attention, motivation, and pleasure. This cascade effect explains why you feel more awake, often happier, and focused after your morning brew.
Short-Term Benefits of Caffeine
Caffeine’s popularity isn’t without merit. Here are some of its most notable short-term benefits:
- Increased energy levels: It helps reduce feelings of fatigue, making it easier to stay active and alert.
- Improved reaction time and focus: Research shows that caffeine can significantly enhance reaction speed and cognitive performance, especially during fatigue (McLellan et al., 2016).
- Boosted mood: Thanks to the dopamine spike, caffeine can temporarily lift spirits and create a sense of well-being.
- Enhanced physical performance: Athletes often use caffeine to improve endurance and mobilize fatty acids as fuel (Spriet, 2014).
Potential Downsides of Caffeine
Of course, it’s not all good news. Regular caffeine consumption has its drawbacks:
- Caffeine crashes: After the initial high, many people experience a sudden dip in energy levels, leading to irritability and fogginess.
- Jitters and anxiety: Caffeine can exacerbate anxiety symptoms, especially in sensitive individuals.
- Sleep disruption: Even if consumed in the early afternoon, caffeine can interfere with melatonin production, disturbing sleep patterns (Clark & Landolt, 2017).
- Tolerance build-up: Over time, your body may become less responsive to caffeine, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects, and potentially leading to dependency.
While caffeine delivers a powerful short-term boost, its long-term benefits for brain health are limited. That’s where nootropics come in.
Read More: 15 Benefits Of Quitting Caffeine – Live Life Caffeine-Free!
What Are Nootropics?

The term “nootropic” was first coined in 1972 by Romanian psychologist and chemist Corneliu E. Giurgea, who defined it as a substance that enhances learning and memory while being safe and neuroprotective (Giurgea, 1972). Unlike caffeine, nootropics aim for sustained cognitive improvement rather than short-lived stimulation.
Nootropics are a broad category of natural and synthetic substances designed to improve brain functions such as memory, creativity, motivation, and focus, without causing significant side effects or dependency. They are cognitive support systems, nourishing and optimizing your brain’s capabilities over time.
Types of Nootropics
There’s a wide variety of nootropics, each offering unique benefits:
Natural Nootropics
- L-Theanine: Found in green tea, it promotes relaxation without sedation and can synergize with caffeine to improve focus.
- Rhodiola Rosea: An adaptogen that enhances resilience to stress and improves stamina and cognitive function (Edwards et al., 2012).
- Bacopa Monnieri: Traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine for memory enhancement and anxiety reduction (Stough et al., 2001).
Synthetic Nootropics
- Modafinil: Originally developed to treat narcolepsy, it’s now a popular off-label for enhancing alertness and cognitive performance (Minzenberg & Carter, 2008).
- Noopept: A peptide-derived compound that improves learning capacity and neuroplasticity.
- Racetams (e.g., Piracetam): These compounds modulate neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, improving learning and memory.
Adaptogens (Nootropic-like Natural Supplements)
- Ashwagandha: Helps regulate cortisol levels and improve stress resilience.
- Lion’s Mane Mushroom: Stimulates nerve growth factor (NGF) production, supporting brain regeneration (Mori et al., 2009).
- Ginseng: Enhances cognitive function and reduces mental fatigue.
How Nootropics Work
Nootropics operate through various mechanisms:
- Neurotransmitter regulation: They balance key chemicals like dopamine, acetylcholine, and serotonin to optimize mood and cognition.
- Enhanced cerebral blood flow: Many nootropics improve blood circulation to the brain, leading to better oxygen and nutrient supply.
- Antioxidant activity: Protecting the brain from oxidative stress and aging, some nootropics act as potent antioxidants.
Unlike caffeine, which primarily stimulates, nootropics nourish, repair, and optimize the brain for long-term cognitive health.
Comparing Nootropics and Caffeine for Focus

Here’s a side-by-side breakdown of how these two contenders stack up:
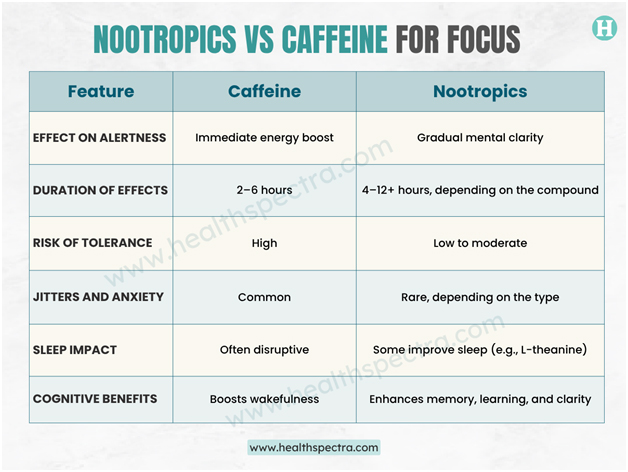 In short, caffeine is like flipping a switch. Nootropics, on the other hand, are more like upgrading your brain’s software—less immediate, but more sustainable.
In short, caffeine is like flipping a switch. Nootropics, on the other hand, are more like upgrading your brain’s software—less immediate, but more sustainable.
Read More: 5 Best Products for Enhancing Mental Focus and Clarity
The Best of Both Worlds: Nootropic + Caffeine Stacks

Nootropic caffeine stacks are a growing trend among high performers, students, and professionals. When combined wisely, caffeine and nootropics can amplify benefits while minimizing drawbacks.
Popular Stacks
1. L-Theanine + Caffeine
Perhaps the most famous combo, L-theanine and caffeine, is often termed the “perfect pair.” L-theanine smooths out caffeine’s rough edges, creating calm alertness.
- Boosts focus and attention.
- Reduces anxiety and jitteriness.
- Enhances mood and cognitive performance.
Research support: A study showed that 97 mg of L-theanine and 40 mg of caffeine significantly improved cognitive performance and reduced mental fatigue (Giesbrecht et al., 2010).
2. Rhodiola + Caffeine
When stress is high and deadlines loom, Rhodiola paired with caffeine can be incredibly effective.
- Supports mental resilience.
- Reduces mental fatigue.
- Prevents burnout under prolonged stress (Spasov et al., 2000).
3. Creatine + Caffeine
While popular among athletes, creatine also supports brain energy metabolism.
- Enhances memory and learning.
- Reduces brain fog.
- Improves reaction speed.
Creatine, combined with caffeine, can provide a powerful physical and mental performance edge, particularly in demanding situations.
Read More: 8 Best Low-Caffeine Pre-Workout Supplements
Stacking Safely: Dosage, Timing, and Tolerance
Stacking is effective only when done mindfully. Here are some rules to follow:
- Start small: Don’t exceed 100 mg caffeine + 200 mg L-Theanine to begin with.
- Cycle your use: Take breaks to avoid building a tolerance.
- Time your intake: Avoid caffeine after 2 p.m. to preserve sleep quality.
- Stay hydrated: Both caffeine and some nootropics can dehydrate you.
- Consult your doctor: Especially if you have heart issues, sleep disorders, or are on medication.
Common Myths About Caffeine and Nootropics
“More caffeine = more focus”
Not true. Higher doses often lead to anxiety, heart palpitations, and reduced productivity.
“Nootropics are magic pills”
They’re not. Think of them as mental supplements that work best with good sleep, a healthy diet, and regular exercise.
“Natural means safe”
Even natural compounds can interact with medications or cause side effects. Do your research.
“All nootropics are stimulants”
Many nootropics are non-stimulating. Some, like L-Theanine or Ashwagandha, actually promote calmness.
Which One Should You Choose?

There’s no clear winner, but here’s how you can decide based on your goals:
Choose Caffeine if:
- You need an instant energy or productivity boost.
- You’re about to hit the gym or tackle a short deadline.
- You tolerate stimulants well and don’t suffer from sleep issues.
Choose Nootropics if:
- You’re looking for natural alternatives to caffeine.
- You want to improve focus, memory, or learning over the long term.
- You’re sensitive to caffeine or have anxiety, sleep disorders, or heart issues.
Choose a Stack if:
- You want the energy of caffeine without the side effects.
- You’re aiming for sustained mental performance throughout the day.
- You want a balanced, holistic approach to brain health.
Who should avoid caffeine altogether? People who experience heart palpitations, sleep disruptions, or heightened anxiety after caffeine consumption should consider cutting back or replacing it with natural cognitive enhancers like L-theanine or Lion’s Mane.
Key Takeaways

- Caffeine is a quick-fix solution—effective but with a price. It can cause jitters, sleep issues, and dependency.
- Nootropics offer long-term brain benefits with fewer side effects. They’re ideal for supporting mental performance and cognitive resilience.
- The best strategy? Try combining both in a thoughtful stack to get the alertness of caffeine and the calm focus of nootropics.
- Your choice ultimately depends on your body’s tolerance, your goals, and your lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
The modern world demands relentless focus, and caffeine and nootropics both offer promising paths toward meeting that demand. Yet, understanding the trade-offs is crucial. Caffeine delivers fast and powerful results, but at the risk of crashes, sleep issues, and dependency. Nootropics, by contrast, build cognitive resilience gradually and offer broader, more sustainable benefits for your brain.
Rather than viewing caffeine and nootropics as opposing forces, the smartest strategy might be to optimize both. Thoughtful stacks combining caffeine with calming nootropics like L-theanine can create a synergistic effect, maximizing energy while minimizing anxiety. For those committed to long-term brain health, nootropics offer a future-focused solution that extends far beyond the buzz of a coffee cup.
Ultimately, your decision should reflect your rhythms, goals, and well-being. Whether you stick with your cappuccino, venture into nootropic territory, or artfully blend both, the path to sharper focus and mental clarity is yours to create. Stay curious, stay balanced, and most importantly—stay focused.
References
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9415189
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5021479
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34035472
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326379
- https://nootropicsexpert.com/nootropics-guide
- https://www.braintropic.com/best-nootropic-stack
- https://www.vogue.in/wellness/content/nootropics-smart-drugs-natural-health-supplement-to-boost-brain-health-memory-focus
- https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/features/nootropics-smart-drugs-overview
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3777290
In this Article