Asthma is a long-term respiratory condition that inflames and narrows the airways, often showing up as wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. While inhalers and medications are the cornerstone of asthma treatment, there’s another piece of the puzzle you may be overlooking—your diet.
Yes, what you eat can make a real difference.
Emerging research is shedding light on the connection between asthma and nutrition, suggesting that certain foods can help reduce inflammation, support lung function, and even minimize flare-ups. Think of it this way: just like food can trigger allergies, the right food can also help soothe and strengthen.
In this article, we’ll dive into the science-backed link between asthma and diet, highlight the best foods that help manage asthma symptoms, and share simple, practical tips to build an asthma-friendly meal plan. Because sometimes, what’s on your plate can help you breathe a little easier.
READ MORE: All About Asthma – Key Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments
The Link Between Diet and Asthma

The foods you eat can either fuel inflammation or help calm it, directly influencing your respiratory health and asthma symptoms.
The Role of Nutrition in Asthma Management
Adopting a nutrient-rich, balanced diet offers several key benefits for people with asthma:
- Strengthens the Immune System: Essential vitamins and minerals help your body fight off infections that could trigger asthma flare-ups.
- Supports Lung Function: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants contribute to healthier lung tissue and reduced inflammation.
- Minimizes Dietary Triggers: Eating fewer processed foods and more whole, antioxidant-rich ingredients may lower the frequency and severity of asthma symptoms.
- Boosts Energy and Resilience: Good nutrition supports overall well-being, which helps in managing chronic conditions more effectively.
Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats have been linked to worsened asthma outcomes:
- Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs): Consumption of UPFs has been associated with increased asthma symptoms and reduced lung function. A study indicated that high UPF intake correlates with a higher prevalence of wheezing and asthma in adolescents. PMC
- High Sugar Intake: Excessive consumption of sugary foods and beverages may increase susceptibility to airway inflammation, thereby exacerbating asthma symptoms. Nature
What the Research Says
Studies have explored how specific nutrients can support asthma management:
- Antioxidants (Vitamins C & E): Known for their anti-inflammatory effects, these may help ease airway inflammation and improve breathing.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Commonly found in fatty fish, omega-3s have been linked to improved asthma control and lung function.
- Vitamin D: Adequate levels may enhance immune response and reduce airway inflammation, potentially decreasing reliance on corticosteroids.
While personal experiences and traditional wisdom offer valuable insights, scientific research provides a solid foundation for understanding how diet influences asthma. Numerous studies have explored the link between nutrition and lung health, confirming that certain foods can either alleviate or aggravate asthma symptoms.
From the anti-inflammatory power of omega-3s to the triggering effects of sulfites and processed foods, here’s what science says about how your plate can impact your lungs.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Asthma Control: Higher Omega-3 Index Is Associated with Better Asthma Control
- Processed Foods and Asthma Symptoms: 5 Foods That May Trigger Asthma Flares
- Diet and Asthma: A Narrative Review
Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Asthma

Asthma is more than just a respiratory condition—it’s a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. And here’s the catch: your diet plays a major role in either turning the heat up on that inflammation or helping to cool it down. While medications are essential, making smart food choices can naturally support your asthma management and reduce flare-ups.
Let’s dive into how eating the right foods can help you breathe easier.
Why Anti-Inflammatory Foods Matter for Asthma
Inflammation is the core culprit behind most asthma symptoms. It narrows the airways, causes tightness in the chest, and leads to coughing or wheezing. So, when we talk about reducing inflammation, we’re talking about lowering the intensity and frequency of those frustrating asthma episodes.
A diet that focuses on anti-inflammatory foods can:
- Ease bronchial constriction.
- Improve lung function.
- Boost overall immunity.
- Reduce dependency on rescue medication.
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Asthma Relief
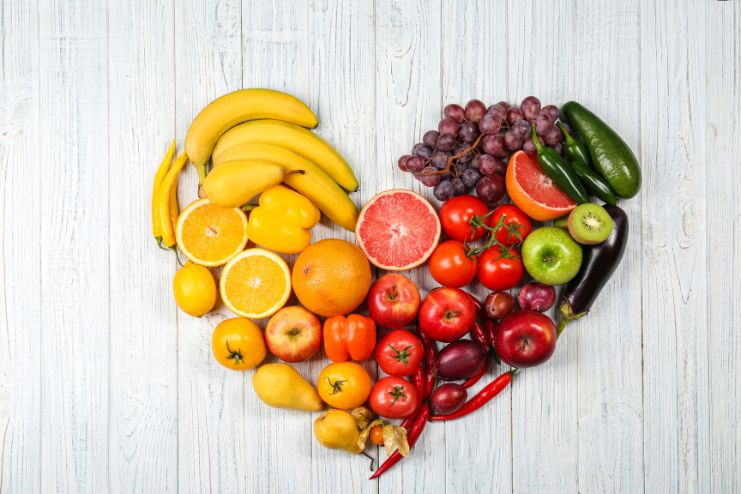

| Food Group | Examples | Key Benefits |
| Fruits & Veggies | Blueberries, spinach, broccoli, sweet potatoes | Antioxidants, vitamins C & E, beta-carotene |
| Healthy Fats | Salmon, flaxseeds, olive oil | Omega-3s to fight inflammation |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, oats, quinoa | Fiber and nutrients without added sugars |
| Lean Proteins | Fish, skinless chicken, beans | Fuel the body without unhealthy fats |
| Anti-inflammatory Spices | Ginger, turmeric | Soothes airways and supports immune health |
| Vitamin D-Rich Foods | Fortified milk, fatty fish, and eggs | Enhances immune response and may reduce flares |
| Nuts & Seeds | Almonds, sunflower seeds, chia seeds | Reduces lung inflammation |
| Leafy Greens | Kale and Swiss chard | Relaxes airway muscles and reduces wheezing |
Foods That Promote Lung Health

When we think about lung health, we usually think of avoiding smoking or pollution. But what we put on our plate can be just as important. Certain foods—especially those rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and anti-inflammatory compounds—can help protect, repair, and strengthen our lungs.
Whether you’re managing a condition like asthma or just trying to breathe a little easier, your diet can be a powerful tool in boosting respiratory wellness.
Why Nutrition Matters for Your Lungs
Lungs are delicate, high-performing organs exposed to everything we breathe in—good or bad. Nutrients not only reduce inflammation (which is key for conditions like asthma or COPD), but they also:
- Support tissue repair.
- Enhance oxygen transport.
- Strengthen immune defenses.
- Keep airways flexible and clear.
In short, the right foods can help you breathe better and longer.
Top Lung-Boosting Nutrients and Where to Find Them
Let’s break down the key nutrients your lungs love and the foods that are packed with them:
1. Vitamin C
- What it does: Strengthens the immune system and reduces airway inflammation.
- Top foods: Strawberries, oranges, kiwi, bell peppers, lemons, and broccoli.
2. Magnesium
- What it does: Helps relax the muscles around the lungs and improves airflow.
- Top foods: Almonds, avocados, pumpkin seeds, spinach, black beans.
3. Beta-Carotene
- What it does: A powerful antioxidant that protects lung tissue from damage.
- Top foods: Carrots, sweet potatoes, mangoes, pumpkins, cantaloupe.
4. Vitamin A
- What it does: Keeps the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract healthy and moist.
- Top foods: Liver, eggs, butter, dark leafy greens, orange vegetables (carrots, squash).
5. Vitamin E
- What it does: Supports immune health and protects lung cells from free radicals.
- Top foods: Sunflower seeds, almonds, hazelnuts, spinach, avocado.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- What they do: Reduce inflammation in the lungs and may improve lung capacity.
- Top foods: Salmon, sardines, mackerel, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts.
Foods to Avoid for Asthma Relief

When it comes to managing asthma, what you don’t eat can be just as important as what you do. Certain foods may trigger inflammation, increase mucus production, or irritate the airways—all of which can worsen asthma symptoms. While triggers vary from person to person, here’s a helpful guide to commonly problematic foods and how to keep them in check.
Common Food Culprits
- Dairy Products: May increase mucus and worsen symptoms in some individuals.
- Processed Foods: Often contain preservatives and additives that trigger inflammation.
- Refined Sugars & Carbs: Can spike inflammation and weaken immunity.
- High-Sodium Foods: Excess salt may tighten airways and inflame lungs.
- Sulfite-Containing Foods: Preservatives in wine, dried fruits, and pickles can provoke asthma attacks.
- Gas-Producing Foods: Can worsen symptoms by increasing pressure on the diaphragm.
- Fried & Greasy Foods: Heavy meals can lead to mucus buildup and sluggish digestion.
- Allergens: Foods like shellfish, nuts, or eggs may trigger allergic asthma.
- Alcohol & Processed Meats: Often contain sulfites and nitrates linked to asthma flare-ups.
How to Manage Food-Related Triggers
Managing asthma through diet isn’t just about eating the right foods—it’s also about avoiding the wrong ones and being mindful of your body’s reactions. Everyone’s triggers can be a little different, so learning how to spot and manage them is key. With a few smart habits, you can stay one step ahead and breathe easier every day.
- Read Labels Carefully: Always check for sulfites, artificial additives, and allergens.
- Cook Fresh at Home: The fewer processed ingredients, the better.
- Keep a Food Diary: Track what you eat and how you feel afterward to spot potential triggers.
- Consult a Specialist: An allergist or dietitian can help you personalize your food plan.
READ MORE: 10 Common Triggers That Could Worsen Your Asthma
The Role of Hydration in Asthma Control

When it comes to managing asthma, we often focus on inhalers, medications, or avoiding allergens—but something as simple as staying well-hydrated can make a big difference, too.
Best Beverages for Lung Support
The right beverages can even provide anti-inflammatory benefits and soothe irritated airways, making them a simple yet powerful addition to your asthma care routine.
- Water – The gold standard for hydration and lung health.
- Herbal Teas – Chamomile, ginger, and licorice tea have natural anti-inflammatory properties that soothe the airways.
- Broth-Based Soups – Warm, hydrating, and nourishing—especially beneficial during flare-ups.
How Hydration Helps Your Lungs
Hydration is more than just a wellness buzzword—it’s a key player in lung health, especially for those managing asthma. When your body is well-hydrated, your airways stay moist, mucus remains thin and easy to clear, and breathing becomes smoother.
Whether it’s hot weather, physical activity, or an asthma flare-up, staying hydrated can make a real difference in how your lungs respond and recover.
- Mucus Thinning: Drinking enough fluids helps keep mucus thin and less sticky. This makes it easier for the lungs to clear out irritants and allergens, reducing the chances of blockages.
- Better Airway Clearance: Thin mucus allows the cilia (tiny hair-like structures lining the airways) to do their job—sweeping away debris and keeping your respiratory tract clean.
- Inflammation Control: Dehydration may trigger the release of inflammatory substances in the body, which can worsen asthma symptoms. Staying hydrated can help counter this and keep inflammation under control.
- Eases Exercise-Induced Asthma (EIB): If physical activity tends to trigger your asthma, dehydration might make it worse. Hydrating before, during, and after exercise can reduce the likelihood of bronchoconstriction.
- Coping with Hot Weather: In hot and humid conditions, your body loses more fluids, increasing the risk of dehydration—which can, in turn, aggravate asthma. Keeping a water bottle handy is key.
- Supporting a Healthy Weight: Hydration supports metabolism and may aid in maintaining a healthy weight. Since obesity is a known risk factor for asthma severity, this is a bonus.
- Reducing Coughing: Some studies suggest a direct link between hydration and reduced coughing, especially in younger individuals with asthma. Water intake can help soothe the throat and minimize dryness-triggered coughs.
Simple Tips for a Lung-Friendly Diet

Managing asthma isn’t just about inhalers and medications—your plate plays a powerful supporting role, too. While diet alone can’t cure asthma, certain foods and eating habits can help reduce airway inflammation, strengthen your immune system, and support long-term lung function.
Here’s a well-rounded approach that combines science-backed strategies with realistic daily practices:
1. Follow a Mediterranean-Inspired Diet
The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats—all of which naturally reduce inflammation and support respiratory health.
Why it helps:
- Loaded with antioxidants and fiber.
- Promotes a healthy gut, which may play a role in immune balance.
- Helps lower overall inflammation levels.
2. Prioritize Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3-rich foods like salmon, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Pro tip: Add fatty fish to your meals 2–3 times a week or sprinkle ground flaxseed into your smoothies or oatmeal.
3. Get Enough Vitamin D
Low levels of vitamin D are linked to worse asthma symptoms in some people. Try to:
- Spend short, safe periods in sunlight.
- Include vitamin D-rich foods like eggs, fortified dairy, and salmon.
- Speak to your doctor about supplementation if needed.
4. Limit Pro-Inflammatory Foods
Some foods may contribute to inflammation and worsen asthma symptoms. Try to reduce:
- Processed meats (like sausages and bacon).
- Sugary snacks and drinks.
- Deep-fried and greasy foods.
- Excessive alcohol.
Instead, opt for whole, fresh foods whenever possible.
5. Eat a Colorful Plate
Each color in fruits and vegetables brings unique antioxidants and nutrients to the table. Think:
- Red (tomatoes, berries): Lycopene and vitamin C.
- Orange/yellow (carrots, pumpkins): Beta-carotene and vitamin A.
- Green (spinach, broccoli): Magnesium, iron, and fiber.
- Purple/blue (blueberries, grapes): Flavonoids and resveratrol.
More colors = more lung-loving protection.
6. Go Whole and Natural
Swap refined products for whole grains, legumes, and minimally processed foods to boost fiber intake and reduce inflammation. Examples:
- Brown rice over white rice.
- Whole wheat bread over white bread.
- Lentils and chickpeas for plant-based, lean protein.
7. Be Mindful of Fats
Not all fats are created equal. Healthy fats like those found in olive oil, nuts, seeds, and avocados can reduce inflammation. Avoid:
- Trans fats (found in many packaged snacks and baked goods).
- Highly processed cooking oils.
A lung-friendly diet doesn’t require drastic changes—just consistent, thoughtful swaps. Eat real, colorful, whole foods. Stay hydrated. Choose quality over quantity. And when in doubt, think, “Will this fuel better breathing?”
Always consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist before making major dietary changes, especially when managing a chronic condition like asthma.
READ MORE: From Yoga to Diet: Natural Strategies to Manage Asthma Effectively
Conclusion
Managing asthma isn’t just about medication—it’s also about everyday choices. The food you eat and the way you hydrate can directly impact your breathing, inflammation levels, and overall lung function. By embracing a nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory diet packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and steering clear of known dietary triggers, you’re giving your lungs the support they deserve.
Don’t forget the simplest and most powerful tool of all: water. Staying hydrated helps keep your airways clear, your mucus thin, and your body better equipped to handle flare-ups.
Think of your lungs as a team player—they show up for you every day. Now it’s your turn to fuel them with the right foods, keep them hydrated, and make lifestyle choices that support easier, fuller, and more peaceful breaths.
References
- https://www.webmd.com/asthma/asthma-diet-what-you-should-know
- https://www.lung.org/blog/asthma-and-nutrition
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/asthma/expert-answers/asthma-diet/faq-20058105
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320233
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7550896/
- https://www.fccmg.com/blog/foods-you-should-and-not-eat-for-healthier-lungs
- https://www.asbestos.com/treatment/nutrition/lung-healthy-foods/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1792828/
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-drink-is-good-for-asthma-5218510
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S001236921535011X
In this Article