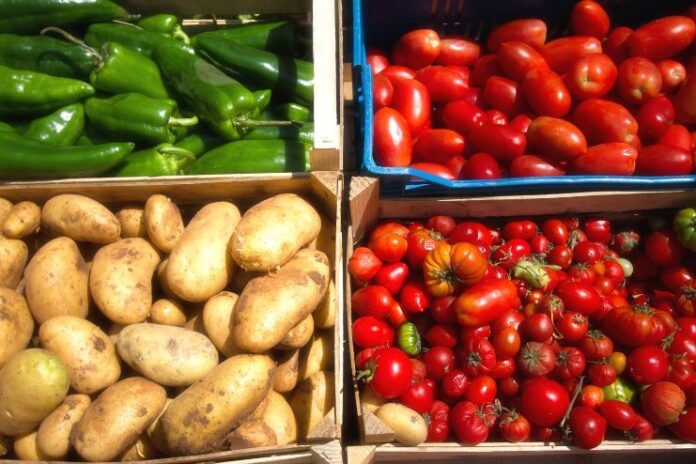
When you think of common vegetables that we use almost daily, nightshades often come to mind. Nightshade vegetables such as tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and peppers are food staples across the globe.
Despite their nutritional benefits, nightshades have been criticized for causing digestive issues and inflammation, raising debate over whether they genuinely impair gut health or are unjustly blamed.
Some people experience bloating, irritable bowel syndrome, or worsened autoimmune conditions following the ingestion of nightshades, raising questions about their contribution to gut health.
This article discusses the science behind nightshade vegetables and their possible impact on digestion. We will also help you with nightshade substitutions, and the perfect way to use them for the best results.

Read More: Nightshade Vegetables – Everything You Need To Know
What Are Nightshade Vegetables?
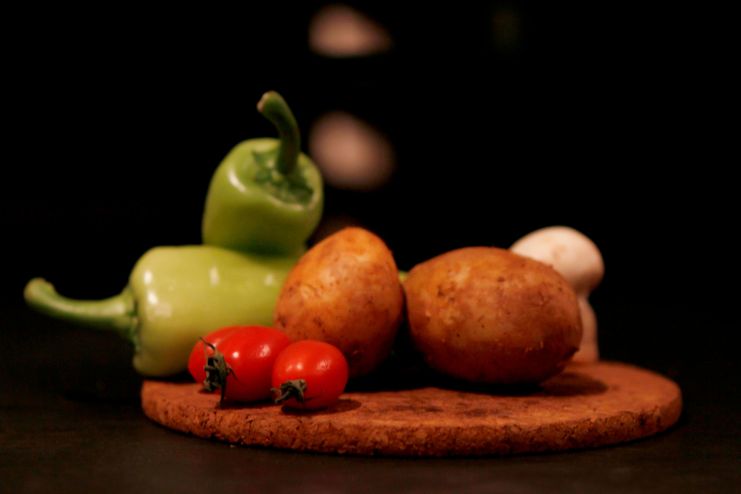

Nightshade vegetables belong to the Solanaceae family, which includes:
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are rich in vitamin C, potassium, and lycopene and are a potent antioxidant with the potential to protect the heart.
- Potatoes: Potatoes contain complex carbohydrates, fiber, and resistant starch, all of which benefit gut bacteria.
- Eggplants: Eggplants are high in fiber, anthocyanins, and antioxidants that benefit brain and cardiovascular health.
- Peppers (bell peppers, chili peppers, and cayenne): All these varieties of peppers are excellent sources of vitamins A and C, as well as capsaicin, which is an anti-inflammatory.
Although nightshades are rich in nutritious compounds, they also have substances such as alkaloids (solanine, capsaicin, nicotine) and lectins, which some believe can be detrimental to gut health.
Read More: The Potato Diet: Can Eating Only Potatoes Help You Lose Weight?
How do Nightshades Affect Gut Health?

Lectins & Alkaloids: Can they Irritate the Gut Lining?
Nightshades produce lectins and alkaloids, which are natural pesticides that defend plants against predators. According to Dr. Robert Kiltz, MD, a board-certified OB/GYN & Reproductive Endocrinologist and founder of CNY Fertility, lectins bind to cell membranes, triggering immune responses that can damage healthy cells, leading to leaky gut syndrome.
Lectins and alkaloids can irritate the gut lining, particularly in individuals with sensitive digestive systems or pre-existing gut conditions. Solanine, an alkaloid in potatoes, is toxic in large quantities and can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.
Leaky Gut Connection: Do Nightshades Contribute to Intestinal Permeability?
Nightshades can cause a leaky gut since they contain lectins and alkaloids. Lectins specifically adhere to the gut wall and thus might increase intestinal permeability.
Alkaloids such as solanine and capsaicin could also cause irritation, especially in people who already have gut issues. Nevertheless, scientific studies on the subject are inconclusive, and although some individuals experience gut discomfort after eating nightshades, others have no problems.
While a few individuals may develop symptoms, nightshades are not a proven cause of leaky gut syndrome.
Read More: Can You Heal a Leaky Gut Naturally? Science-Backed Solutions for Better Gut Health
Impact on Gut Microbiome: Do They Support or Disrupt Healthy Bacteria?
Nightshades are a source of fiber and resistant starch, which can promote beneficial gut bacteria. Some people might, nonetheless, experience bloating or discomfort from nightshades because of their alkaloid and complex carbohydrate content.
Do Nightshades Trigger IBS, Bloating, or Digestive Discomfort?
Individuals with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or sensitivities may experience bloating or cramping after consuming nightshades. When gut bacteria ferment fiber and resistant starch, they can produce gas, leading to discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Nightshades and Inflammation: Myth or Reality?
The link between nightshades and inflammation is still controversial. Anecdotal evidence suggests that nightshades worsen symptoms in individuals with autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and Crohn’s disease.
Although some people believe that removing nightshades reduces inflammation, there is no scientific evidence that proves nightshades are inflammatory. Studies suggest that individual responses might vary and that overall diet and gut health greatly influence inflammation.
Read More: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, And Treatment
Who should avoid Nightshades?
The following individuals might find it helpful to avoid or limit nightshade consumption:
- Individuals with IBS, leaky gut syndrome, or a sensitivity to alkaloids and lectins.
- Some individuals with autoimmune diseases might experience worsened symptoms, although there is no scientific evidence to support this.
- Nightshades should be avoided by individuals with food sensitivities or intolerances. They should also be avoided by those who experience bloating, cramping, or other gastrointestinal symptoms after eating
If you believe nightshades are aggravating your symptoms, eliminating them from your diet can help determine if they are a trigger.
Are Nightshades Beneficial for Health?

Despite concerns, nightshades have numerous health benefits.
- Rich in Antioxidants: Tomatoes and peppers are rich in lycopene, vitamin C, and flavonoids that aid immune function and lower oxidative stress.
- Promote Heart Health: Potatoes are rich in potassium, which helps maintain blood pressure.
- Improve Vision and Immune Function: Peppers are rich in vitamin A, a nutrient essential for eye health and immune function.
For most people, the advantages of nightshades exceed the potential dangers, especially if well tolerated.
Read More: Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods To Counter Inflammation
How to Reduce the Negative Effects of Nightshades?
If you are experiencing a slight discomfort due to nightshades but don’t want to exclude them entirely, try the following strategies:
- Cooking Methods: Boiling, roasting, and fermenting nightshades reduces alkaloid levels, making them easier to digest.
- Pairing with Gut-Friendly Foods: Consuming nightshades with fiber-dense and probiotic foods may ease digestion.
- Adding Gut-Healing Foods: Bone broth, fermented foods, and high-fiber options can help maintain gut health and reduce sensitivity.
Nightshade Substitutes for a Gut-Friendly Diet

For those who prefer to steer clear of nightshades, some substitutes are as follows:
- Tomato Replacements: Carrot, beet, or pumpkin sauce.
- Potato Substitutions: Sweet potatoes, cauliflower, or parsnips.
- Pepper Substitutes: Radishes, cucumbers, or herbs such as basil and parsley.
If you’re sensitive to nightshades, the list above offers simple and nutritious substitutes to support your diet. However, if you tolerate them well, there’s no reason to avoid them.
Enjoy nightshades in the ways we’ve suggested to maximize their health benefits and support overall gut health.
Conclusion

Some people find Nightshade vegetables difficult to digest, but most people tolerate them well. If these vegetables seem to cause serious health issues, consider eliminating them from your diet temporarily to determine whether they’re a trigger.
The most important thing is to have a balanced diet. How nightshades impact digestion also depends on cooking techniques, serving sizes, and each person’s unique gut. If these vegetables agree with you, then eat them in moderate quantities.
Listen to your body and choose what works best for you!
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37202602/
- https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/digestive-health/good-foods-to-help-your-digestion/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11316282/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37202602/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9976781/
- https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/healthy-living/nutrition/anti-inflammatory/how-nightshades-affect-arthritis
- https://www.doctorkiltz.com/plant-toxins/
In this Article